Given a binary tree, write a code to serialize and deserialize binary tree.
You can choose any algorithm for serialization and deserialization of a binary tree. But make sure the algorithm we choose to serialize a binary tree to a string and can also deserialize the string representation to the original tree structure.
What is serialization and deserialization?
Before solving this problem, let’s first understand what is serialization and deserialization?
In Serialization, the data structure or object is translated/converted into a sequence of bits so that it can be stored in a file or memory buffer, or transmitted across a network.
Deserialization is the process to reconstruct the data structure or object from the sequence of bits.
As per the problem statement, we are free to choose any algorithm for serialization and deserialization of a binary tree. So, which algorithm do we choose and why?
For serialization, we have to first traverse a binary tree. Traversing a binary tree means visiting each node of a binary tree exactly once. It can be done through the depth-first (preorder, postorder and inorder) or breadth-first (level order) manner.
Binary tree preorder traversal
Binary tree level order traversal
Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree – Java Code
Here, we are going to solve this problem using level order traversal. You can also use preorder and inorder traversal.
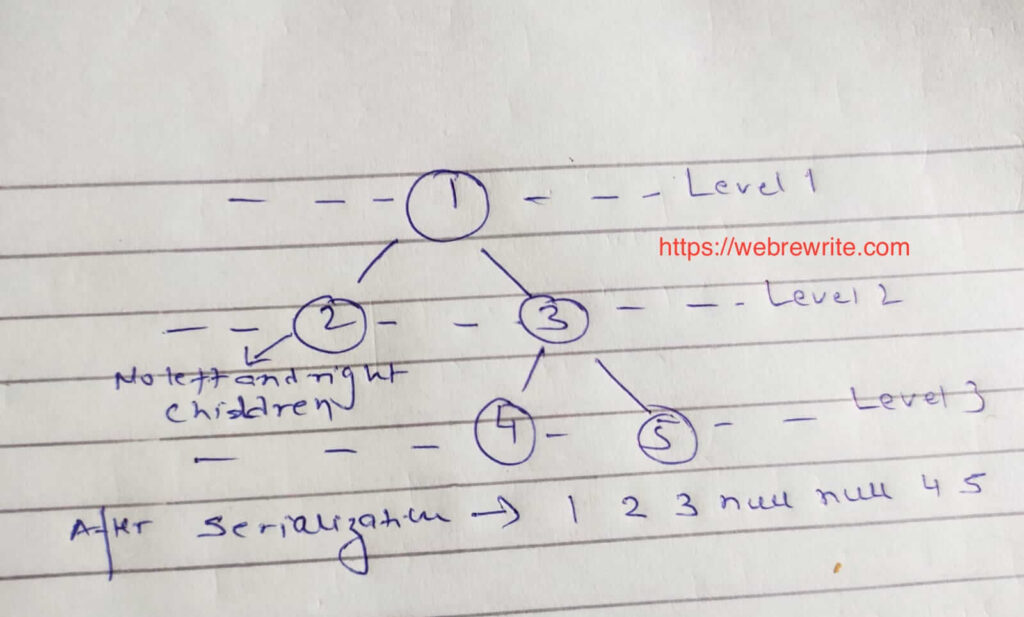
In level order traversal, we visit each node of a tree level by level.
When we do the serialization, we traverse a binary tree level by level. We pick each node value and append it in a string separated by a space. If the value of the node is null then we append null in a string.
In deserialization, we take the serialized string and reconstruct the binary tree back.
The time complexity of this approach is O(n) and its space complexity is also O(n).
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 |
//Serialize and deserialize a binary tree public class Codec { // Level order traversal. public String serialize(TreeNode root) { if(root == null) { return ""; } Queue<TreeNode> qu = new LinkedList<>(); qu.add(root); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); while(!qu.isEmpty()) { TreeNode temp = qu.poll(); if(temp == null) { sb.append("null "); } else { sb.append(temp.val+" "); qu.add(temp.left); qu.add(temp.right); } } return sb.toString().trim(); } // Deserialize a binary tree. public TreeNode deserialize(String data) { if(data == "") return null; //Split string String[] vals = data.split(" "); if(vals.length == 0) return null; Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>(); //First value is root node TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(vals[0])); q.add(root); TreeNode p = null; String val; int i = 1; //Run a loop and traverse the array while(i < vals.length) { p = q.poll(); val = vals[i++]; if(val.equals("null")) { p.left = null; } else { p.left = new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(val)); q.add(p.left); } if(i < vals.length) { val = vals[i++]; if(val.equals("null")) { p.right = null; } else { p.right = new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(val)); q.add(p.right); } } } return root; } } |