In this tutorial, I am going to discuss the Single Responsibility Principle of SOLID design principles.
I am going to discuss what is Single Responsibility Principle? How does this principle help us to write clean and maintainable code?
SOLID principles are made popular by Robert C. Martin. You can read his amazing book clean architecture.
Single Responsibility Principle
This principle states that a class should have only one reason to change.
Multiple reasons for change indicate a class has many responsibilities. A class that has many responsibilities is harder to maintain and also it increases the possibility of bugs.
To understand this principle, let’s take an example.
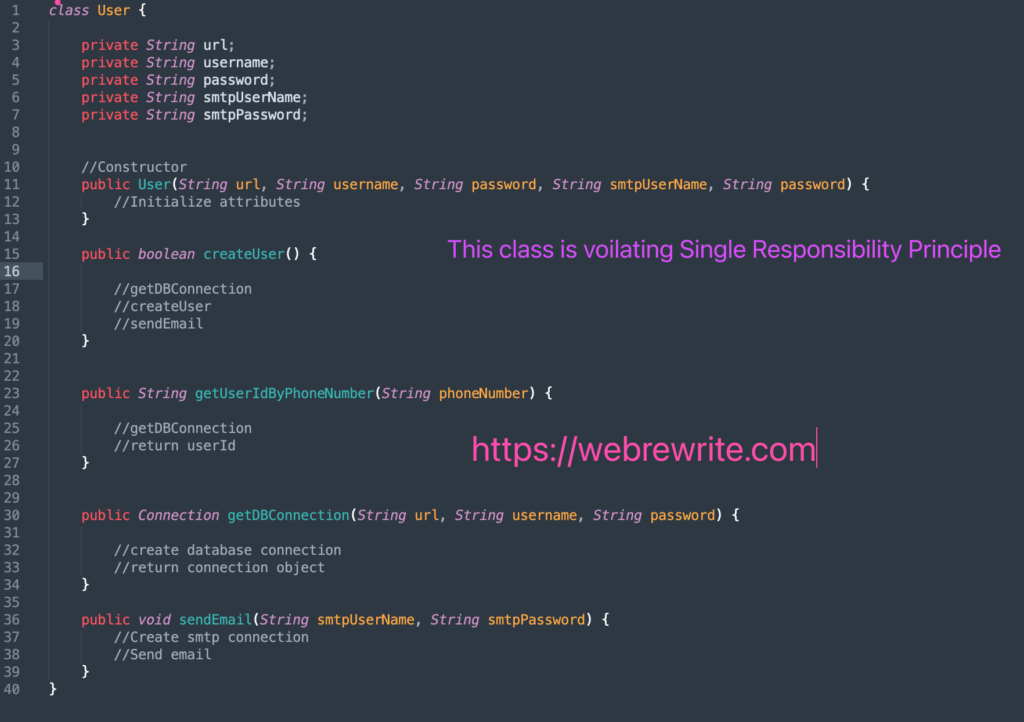
For this I am creating a class user, In this class, we are creating a new user and also fetching the userId by phone number.
But If you look at this class apart from creating a new user and fetching the userId. This class is also responsible for creating a database connection object and sending an email.
So, the User class has more than one responsibility. It’s violating the Single Responsibility Principle. Having multiple responsibilities creates a maintenance nightmare.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 |
//User class voilating SRP, It has too many responsibilities class User { private String url; private String username; private String password; private String smtpUserName; private String smtpPassword; //Constructor public User(String url, String username, String password, String smtpUserName, String password) { //Initialize attributes } public boolean createUser() { //getDBConnection //createUser //sendEmail } public String getUserIdByPhoneNumber(String phoneNumber) { //getDBConnection //return userId } public Connection getDBConnection(String url, String username, String password) { //create database connection //return connection object } public void sendEmail(String smtpUserName, String smtpPassword) { //Create smtp connection //Send email } } |
Any change in database connection and send email leads to change in User class.
Creating a database connection and sending an email is not the responsibility of a User class. A user class should only be responsible for creating a new user and getting userId by phone number.
User class should not bother about creating the database connection and how to send an email. These two responsibilities should be moved to a separate class. Considering these points, let’s refactor the code.
Classes which follow Single Responsibility Principle – Java Code Example
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
//User class after refactoring the code class User { //Class responsible for creating db connection private DBConnection dbConnection; //Class responsible for sending an email private EmailService email; //Constructor public User(DBConnection dbConnection, EmailService email) { //Initialize attributes } public boolean createUser() { //getDBConnection //createUser //sendEmail } public String getUserIdByPhoneNumber(String phoneNumber) { //getDBConnection //return userId } } |
The responsibility for creating a database connection should be moved to a different class. The new DBConnection class should be responsible for creating a database connection object.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
//Class responsible for creating a database connection class DBConnection { private String url; private String username; private String password; public Connection getDBConnection(String url, String username, String password) { //create database connection //return connection object } } |
Similarly, sending an email is also a separate responsibility. EmailService class should be responsible for sending an email.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
//Email service class class EmailService { private String smtpUserName; private String smtpPassword; public void sendEmail(String smtpUserName, String smtpPassword) { //Create smtp connection //Send email } } |
Now, When responsibility is segregated you can clearly see the difference. Each class is focused and responsible for doing one thing. In the future, if there comes a change related to the user, database connection, and sending an email only the class which is responsible for that functionality will be modified.
How to create immutable class in java
Conclusion
The Single Responsibility Principle ensures that our classes should be responsible for a single functionality.