Given a binary tree, we have to write a code to print the right view of a binary tree.
Right View of a Binary Tree
The right view of a binary tree is the set of visible nodes when it is visited or seen from the right side.
For example:
Example 1:
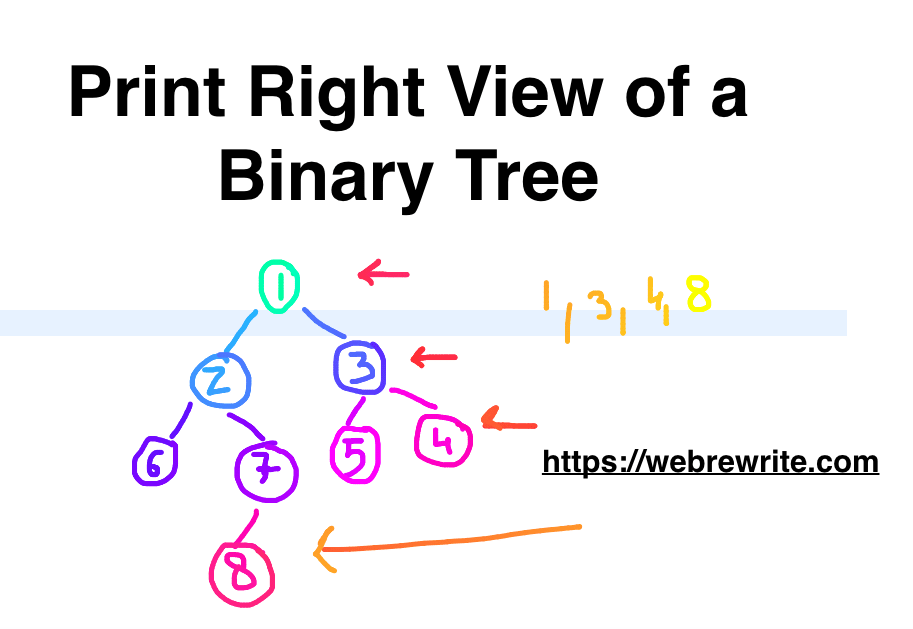
Let’s take an example. In this binary tree, the node which is visible from the right side is 1, 3, 4, and 8.
Example 2:
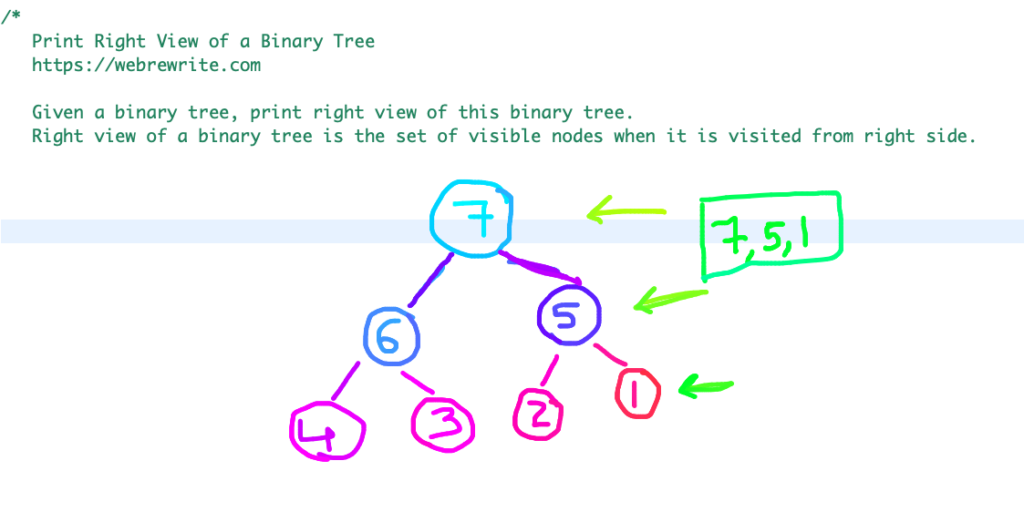
In the second example, the node which is visible from the right side is 7, 5, and 1.
We have discussed the problem statement with multiple examples. Before checking the solution, think about how you can approach this problem? Which data structure do you use to solve this problem.
At the end of this post, I have shared the link to the video tutorial.
Right View of a Binary Tree using Queue – Java Code
In this example, I have explained how to print the right view of a binary tree using level order traversal of a binary tree.
The idea here is to traverse a binary tree using level order traversal and print the last node of each level.
Here are the following steps:
i) Declare a queue and add a root node in a queue.
ii) Run a while loop while the queue is not empty and do the following steps
a) Find the length (no. of nodes present in a queue).
b) Run a loop from 0 to length-1.
c) Poll a node from the queue and check if it’s the last node of that level. If it’s then print the node value.
d) Add the left and right child of a node in a queue. If it’s not null.
iii) Repeat these steps until the binary tree is traversed completely.
The time and space complexity of this approach is O(n). This problem is similar to the print left view of a binary tree.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 |
//Print right view of a binary tree - Java Code public class TreeRightView { public static class TreeNode { int data; TreeNode left; TreeNode right; TreeNode(int data) { this.data = data; } } public static void rightView(TreeNode root) { if(root == null) { return; } //Declare a queue and add a root node Queue<TreeNode> qu = new LinkedList<>(); qu.add(root); //While queue is not empty while(!qu.isEmpty()) { //no. of record present in a queue int len = qu.size(); for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) { TreeNode node = qu.poll(); //Print last record of each level if(i == len-1) { System.out.println(node.data); } if(node.left != null) { qu.add(node.left); } if(node.right != null) { qu.add(node.right); } } } } public static void main(String[] args) { rightView(createBinaryTree()); } public static TreeNode createBinaryTree() { TreeNode rootNode = new TreeNode(7); rootNode.left = new TreeNode(6); rootNode.right = new TreeNode(5); rootNode.left.left = new TreeNode(4); rootNode.left.right = new TreeNode(3); rootNode.right.left = new TreeNode(2); rootNode.right.right = new TreeNode(1); return rootNode; } } |
Binary Tree Right Side View LeetCode Solution
In this section, let’s discuss the LeetCode solution to a similar problem. The idea is the same, we do the level order traversal and pick the last node of each level.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 |
//Right vew of a binary tree leetcode solution class Solution { public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>(); if(root == null) { return result; } Queue<TreeNode> qu = new LinkedList<>(); qu.add(root); while(!qu.isEmpty()) { int len = qu.size(); for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) { TreeNode temp = qu.poll(); if(i == len-1) { result.add(temp.val); } if(temp.left != null) { qu.add(temp.left); } if(temp.right != null) { qu.add(temp.right); } } } return result; } } |
Binary tree right side view video tutorial
In this video tutorial, I have explained how we can print the right view of a tree using a queue.