Write a java code to check balanced parentheses in an expression using stack.
Given an expression containing characters ‘{‘,’}’,'(‘,’)’,'[‘,’]’. We have to write a code to check whether an input string has valid parentheses.
An input string is valid if:
Open brackets must be closed by the same type of brackets.
Open brackets must be closed in the correct order.
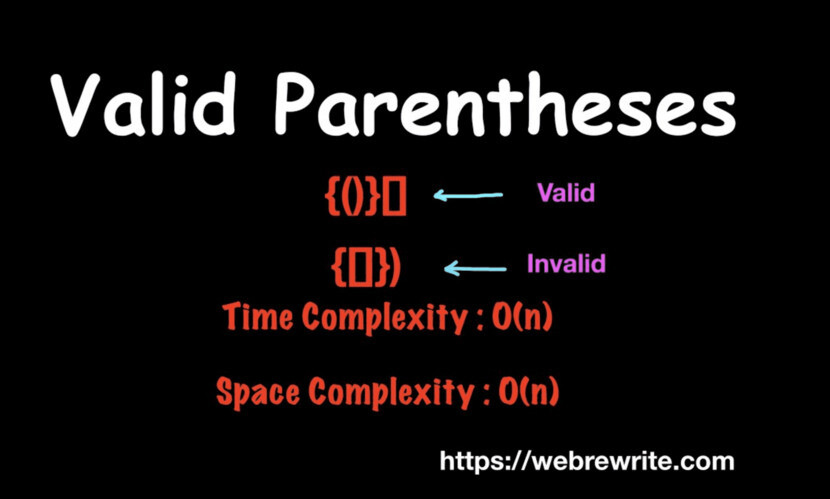
Example –
i) {[]}) – Invalid
ii) {()}[] – Valid
For solving this kind of problem the choice of data structure is very important. Think for a moment which data structure should we choose to solve this problem?
Also, at the end of this tutorial i have shared a video tutorial link.
Algorithm to check Balanced Brackets
In this tutorial, i am using stack data structure to solve this problem efficiently. Here are the following steps to solve this problem.
i) First, we need to traverse an input string and pick each character at a time.
ii) If the current character is starting bracket ‘{‘, ‘(‘, ‘[‘ then push it in a stack.
iii) If the current character is closing bracket ‘}’, ‘)’, ‘]’ and the top of the stack is starting bracket then pop from the stack.
iv) After complete traversal, if the stack is empty then it is balanced parentheses otherwise it is not balanced.
Java Program to Reverse a String using Stack
Find Next Greater Element in an Array
Check Balanced Parentheses in an Expression using Stack – Java Code
We have discussed the algorithm to solve this problem. Let’s write a java code to implement this algorithm using stack data structure.
The time complexity of this approach is O(n) and it’s space complexity is also O(n).
Find the minimum element in a stack in O(1)
Find maximum element in a stack in O(1)
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 |
/** * Balanced Brackets Problem - https://webrewrite.com */ import java.util.Stack; public class ParenthesesChecker { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "{[]})"; //Declare a stack Stack st = new Stack<>(); //Traverse a string for(int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) { /* If the current character is starting bracket, then push them in a stack */ if(str.charAt(i) == '{' || str.charAt(i) == '[' || str.charAt(i) == '(') { st.push(str.charAt(i)); /* Else, If the stack is not empty, And current character is a closing bracket and top character of a stack is matching open bracket then pop it. */ } else if ( !st.empty() && ((str.charAt(i) == ']' && st.peek() == '[') || (str.charAt(i) == '}' && st.peek() == '{') || (str.charAt(i) == ')' && st.peek() == '('))) { st.pop(); } else { st.push(str.charAt(i)); } } if(st.empty()) { System.out.println("Balanced"); } else { System.out.println("Not balanced"); } } } |
Valid Parentheses LeetCode Solution
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
//Valid Parentheses Solution public boolean isValid(String s) { Stack st = new Stack<>(); for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { Character ch = s.charAt(i); if(!st.isEmpty() && ch == '}' && st.peek() == '{') { st.pop(); } else if(!st.isEmpty() && ch == ')' && st.peek() == '(') { st.pop(); } else if(!st.isEmpty() && ch == ']' && st.peek() == '[') { st.pop(); } else { st.push(ch); } } if(st.isEmpty()) { return true; } return false; } |