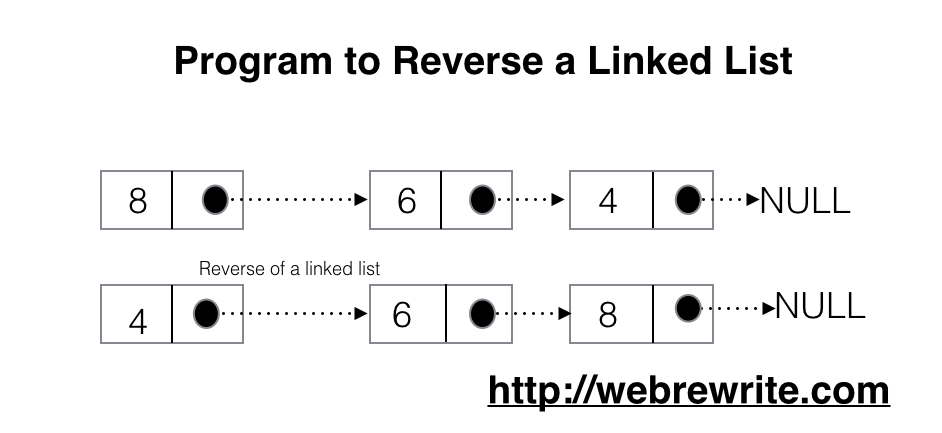
Write a C program to reverse a linked list. Given a singly linked list, we have to write a code to reverse a linked list. In this tutorial, we are going to use iterative approach to solve this problem.
There are two ways to reverse a linked list. We can reverse a linked list using an iterative approach or we can reverse a linked list using recursion. Both approaches are very important in terms of interviews. So make sure you understand both the concepts and practice it very well.
C Program to Reverse a linked list using recursion
If you are not familiar with iterative and recursive approach then check my previous tutorial on Recursion vs iteration.
|
1 2 3 |
Input - 8->6->4 Output - 4->6->8 |
Algorithm to Reverse a Linked List
1. Traverse a linked list.
C program to count number of nodes in a linked list
2. Declare a three-pointers prev, next and current of a node type. The current pointer points to head. Using current pointer traverse a linked list until current node is not null. Change the links (or pointer to reverse a linked list).
The time complexity to reverse a linked list is O(n).
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 |
//Method to reverse a linked list void reverse(){ /* Declare pointer to node type. */ struct node *prev, *next, *current; /* Points to head.*/ current = head; /* Initialize prev pointer to NULL. */ prev = NULL; /* While it's not point to NULL. */ while(current != NULL){ /* Points to next node . */ next = current->next; /* Points to prev.So the first element points to NULL which becomes last when we reverse a linked list.*/ current->next = prev; prev = current; current=next; } /* Assign to head. */ head = prev; } |
C Program to Reverse a Linked List
We have discussed the algorithm to reverse a singly linked list. Let’s write a c code to implement an algorithm to reverse a singly linked list.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 |
#include <stdio.h> /* Declare node .*/ struct node{ int data; struct node* next; }; struct node* head; void insert_node(int data){ /* Allocate new node using malloc. */ struct node* newnode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node*)); /* Data and link to next node. */ newnode->data = data; newnode->next = head; head = newnode; } void reverse(){ struct node *prev, *next, *current; current = head; while(current!=NULL){ next = current->next; current->next = prev; prev = current; current=next; } head = prev; } void print(){ struct node* p; p = head; while(p != NULL){ printf(" %d\n ", p->data); p = p->next; } printf("\n"); } int main() { head = NULL; insert_node(2); insert_node(4); insert_node(6); printf("Linked list before calling reverse \n"); print(); reverse(); printf("Linked list after calling reverse \n"); print(); return 0; } |
Output :
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
Linked list before calling reverse 6 4 2 Linked list after calling reverse 2 4 6 |
I have tried my best to explain how to reverse a singly linked list in a very simple and easy way. If you still have any doubt and you want to share another approach with our readers then you can let us know through your comments.