In this problem, We have to write a code to sort a stack using recursion. We have to sort in a descending order (Top of the stack has the greatest element).
We don’t have to use any loop constructs ( for, while etc) or additional data structure.
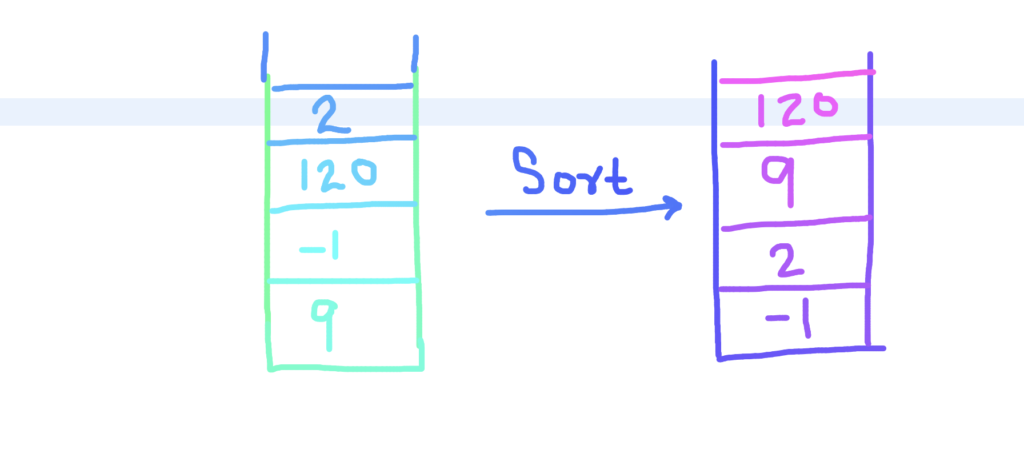
For Example –
In this example, You can see after sorting the stack, the element which has greater value is at the top of the stack.
This question is similar to reverse a stack using recursion. In this problem we don’t have to use extra stack to solve this problem. Before checking the solution, first try to solve this problem yourself.
At the end of this tutorial, I have also mentioned the video tutorial link.
Programming Questions on Stack
Sort a Stack using Recursion – Java Code
We know in a stack the element which we pushed at last is the first element to be popped out. It follows Last In First Out (LIFO) order.
To sort a stack, First we have to pop all the values of a stack recursively until the stack becomes empty. And then insert each values at correct position so that the stack will be sorted.
It means we have to use two recursive function to solve this problem.
The time complexity of this approach is O(n^2) and it’s space complexity is O(n).
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 |
//Sort a Stack using Recursion - Java Code public class SortStack { public static void sort(Stack<Integer> st) { if(st.isEmpty()) { return; } int temp = st.pop(); sort(st); insertAtCorrectPosition(st, temp); } public static void insertAtCorrectPosition(Stack<Integer> st, int temp) { if(st.isEmpty() || st.peek() < temp) { st.push(temp); return; } int elem = st.pop(); insertAtCorrectPosition(st, temp); st.push(elem); } public static void main(String[] args) { Stack<Integer> st = new Stack<>(); st.push(9); st.push(-1); st.push(120); st.push(2); System.out.println(st); sort(st); System.out.println(st); } } |