Given a singly linked list, write a code to reverse a linked list. In this tutorial, you are going to learn how to reverse a linked list in java using iterative approach.
For example –
Input linked list.
15 -> 9 -> 8 -> 5 -> NULL
When we reverse this linked list then the output is given below.
5 -> 8 -> 9 -> 15 -> NULL
In input linked list, head points to a node whose value is 15 but when it’s reversed the head points to a node whose value is 5.
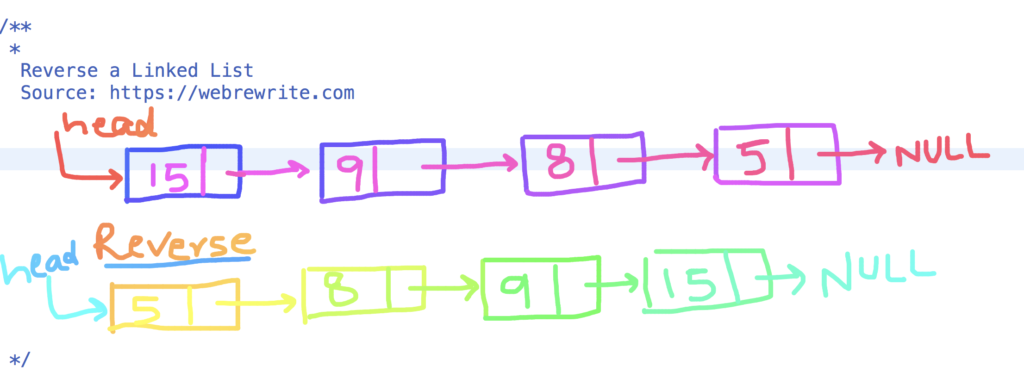
We can reverse a linked list by using either iterative or recursive approach. In this tutorial, I am going to focus mainly on iterative approach to reverse a singly linked list.
Reverse a Linked List in Java
To reverse a linked list in-place, what we have to do is to reverse the pointers such that the next element points to the previous node.
Here are the following steps –
i) Declare three variables previous, curr and temp.
ii) Traverse a linked list while curr is not null. Then Save the next Node of the current element in the temp pointer.
iii) Set the next of the current Node to the previous. Then shift previous to current and current element to temp (which is next).
Remove duplicates from a sorted linked list
I have explained this approach using video tutorial, the link of that video tutorial is present at the end of this post.
The time complexity of this approach is O(n) and it’s space complexity is O(1).
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 |
/* Reverse a linked list java code */ //Node Class public class Node { int data; Node next; public Node(int data) { this.data = data; this.next = null; } } //Actual Implementation public class ReverseLinkedList { //Insert node at head public Node insertAtHead(Node head, int data) { if (head == null) { head = new Node(data); } else { // Create a new node Node temp = new Node(data); // New node points to head temp.next = head; // Head points to a new node head = temp; } return head; } public Node reverseLinkedList(Node head) { Node previous = null; Node curr = head; Node temp = null; while (curr != null) { temp = curr.next; curr.next = previous; previous = curr; curr = temp; } return previous; } public void print(Node head) { Node temp = head; while (temp != null) { System.out.print(temp.data + " -> "); temp = temp.next; } System.out.print("null"); System.out.println(" "); } public static void main(String[] args) { Node head = null; ReverseLinkedList ll = new ReverseLinkedList(); head = ll.insertAtHead(head, 5); head = ll.insertAtHead(head, 8); head = ll.insertAtHead(head, 9); head = ll.insertAtHead(head, 15); System.out.println(" Linked List "); ll.print(head); Node reverse = ll.reverseLinkedList(head); System.out.println(" Reverse Linked List "); ll.print(reverse); } } |
In this video tutorial, I have explained how we can reverse a linked list using iterative approach.