In this tutorial, I am going to discuss a programming question how to segregate even and odd nodes in a linked list or odd even linked list.
Given a singly linked list, We have to write a code to group all odd nodes together followed by the even nodes. We have to group based on node number not the value present in the node.
Try to solve this problem in O(n) time complexity and O(1) space complexity where n is the no. of nodes in a linked list.
Also, the relative order inside both the even and odd groups should remain as it was in the input. The first node is considered odd, the second node even and so on …
For example –
In the this example, Given input linked list is
1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> NULL
When we segregate even and odd nodes in a Linked List then the output is
1 -> 3 -> 2 -> 4 -> NULL
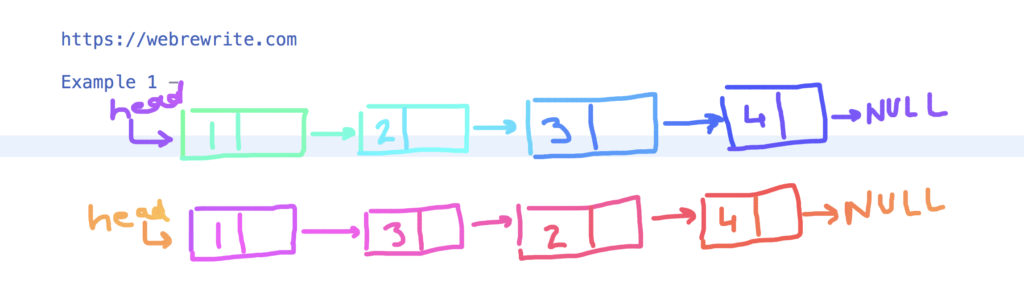
Odd Even Linked List Example
Let’s discuss how we can solve this problem. As per the problem statement we have to solve this problem in O(n) time complexity and by using constant space.

We will start with the easiest approach and finally we solve this problem in given time and space constraint.
Programming Questions on Linked List
Segregate Even and Odd Nodes in a Linked List – Java Code
The easiest way to solve this problem is to create a new list. Traverse a singly linked list and than put the odd index nodes first then traverse a linked list again to put the even index nodes.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 |
//Segregate odd and even linked list public ListNode oddEvenList(ListNode head) { //Temp pointer points to head ListNode temp = head; //Head pointer for a new list ListNode result = new ListNode(); /*OddEvenNode pointer points to head initially * We use this pointer as an iterator. */ ListNode oddEvenNode = result; int count = 1; //Put the odd nodes first while(temp != null) { if(count % 2 == 1) { oddEvenNode.next = new ListNode(temp.val); oddEvenNode = oddEvenNode.next; } temp = temp.next; count++; } //Reintialize the values temp = head; count = 1; //put the even nodes while(temp != null) { if(count % 2 == 0) { oddEvenNode.next = new ListNode(temp.val); oddEvenNode = oddEvenNode.next; } temp = temp.next; count++; } oddEvenNode.next = null; return result.next; } |
Check if a linked list is palindrome or not
Remove Nth node from the end of a linked list
Even After Odd Linked List – Java Code
In our previous approach, we have solved this problem using two traversal. Let’s think how we can solve this problem in a single traversal. We can solve this problem in single traversal by taking two list.
The idea here is to separate the linked list into two parts, even and odd list. The separation is based on index. The index is started from 1. Traverse a linked list and put odd and even nodes separately by maintaining it’s relative order. At the end we can combine both the list.
The time complexity of this approach is O(n) and it’s space complexity is also O(n).
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 |
//Even After Odd Linked List - Java Code public ListNode oddEvenListSecond(ListNode head) { //Dummy nodes for even and odd head ListNode oddHead = new ListNode (); ListNode evenHead = new ListNode (); //Odd pointer points to oddHead ListNode odd = oddHead; //Even pointer points to evenHead ListNode even = evenHead; //Temp pointer points to the head of a linked list ListNode temp = head; /*Initialize count with 1, As we have * to start the index from 1. */ int count = 1; /*Traverse a linked list and put the odd index nodes * in odd list and even index nodes in even list. */ while(temp!= null){ if(count%2 == 1) { odd.next = new ListNode(temp.val); odd = odd.next; } else { even.next = new ListNode(temp.val); even = even.next; } //Move the temp pointer temp =temp.next; //Increment the value of count count++; } //Merge even nodes after odd odd.next = evenHead.next; /*Assign null address which indicates end * of a list. */ even.next = null; return oddHead.next; } |
Odd Even Linked List LeetCode Solution – Java Code
Now, let’s discuss our final approach in which we solve this problem by using constant space.
The idea here is to use two pointers (even and odd). The odd pointer points to odd nodes and even pointer points to even node. In this way, by doing pointer manipulation we can solve this problem.
Time complexity O(n).
Space Complexity O(1).
Find the intersection of two linked lists
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 |
//Odd Even Linked List public ListNode oddEvenListThird(ListNode head) { if (head == null) return null; //Odd pointer points to head node ListNode odd = head; /* * Even pointer points to head.next * If first node is odd then the second node will be even. */ ListNode even = head.next; /* * EvenHead pointer points to even node */ ListNode evenHead = even; /* * If even pointer does not point to null * and even.next does not point to null. */ while (even != null && even.next != null) { odd.next = even.next; odd = odd.next; even.next = odd.next; even = even.next; } odd.next = evenHead; return head; } |