Get minimum element from stack in O(1).
In this problem, we have to design a stack that supports push, pop, top, and retrieving the minimum element in constant time (O(1)).
push(x) — Push element x onto stack.
pop() — Removes the element on top of the stack.
top() — Get the top element.
getMin() — Retrieve the minimum element in the stack.
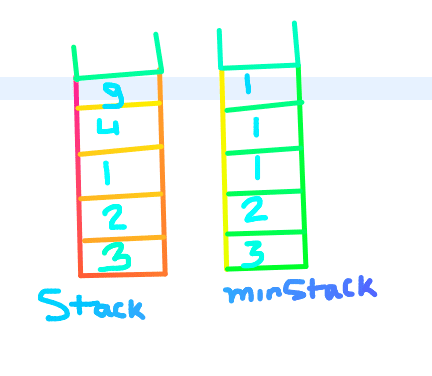
For example: Suppose, If we push the following elements in a stack.
9 ==> Top
1
2
3
Then if we call getMin() method, It should return 1 in O(1) (constant time).
In a stack data structure, Element which we pushed at last is the first element to be popped out. That’s why it is also known as LIFO (Last In First Out) data structure.
Now, Think how we can design a stack that supports getMin() in constant time (o(1)). At the end of this tutorial, i have mentioned the link of a video tutorial.
How to Design Min Stack to Get Minimum Element from Stack
We can solve this problem of min stack by using two stacks.
i) Declare two stacks. One is the main stack in which we push value as it is. In the second stack, we only push the minimum element present at that time.
|
1 2 |
Stack st = new Stack<>(); Stack minStack = new Stack<>(); |
ii) Whenever we perform push operation in a stack.
a) Push the value as it is in a first stack.
b) For the second stack, push only the minimum value. For minimum value, Compare the current value with the value present at the top of the stack.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
//Stack push operation public void push(int data) { //Assign the value we need to push in a min variable int min = data; //If minStack is not empty and the value we need to push is greater // than the value from the top of a stack if(!minSt.isEmpty() && min > minSt.peek()) { //the we assign the top value of a stack min = minSt.peek(); } st.push(data); minSt.push(min); } |
After the push operation, both the stack will look like this.
Now, if peek() method is called on the second stack then we get the min element in O(1).
Find the Minimum Element in a Stack in O(1) – Java Code
We have discussed how we can design a min stack that supports getMin() operation in O(1). Let’s write a java code to implement this logic.
Find next greater element in an array
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 |
//Java program to implement getMin() in O(1). import java.util.Stack; public class MinStack { private Stack<Integer> st; private Stack<Integer> minSt; public MinStack() { st = new Stack<>(); minSt = new Stack<>(); } public void push(int data) { int min = data; if(!minSt.isEmpty() && min > minSt.peek()) { min = minSt.peek(); } st.push(data); minSt.push(min); } public void pop() { st.pop(); minSt.pop(); } public int top() { return st.peek(); } public int getMin() { return minSt.peek(); } public static void main(String[] args) { MinStack minElem = new MinStack(); minElem.push(4); minElem.push(5); minElem.push(8); minElem.push(1); minElem.pop(); System.out.println(" Minimum Element from Stack " + minElem.getMinimum()); } } |
In this video tutorial, I have explained how to find min element in a stack each time while elements are being pushed and popped.