In this tutorial, i am going to explain how to find the intersection of two linked lists.
Given the heads of two singly linked lists. We have to write a code to find the intersection point of two linked lists. If no intersection point is found then return null.
You may assume there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure. We have to solve this problem in O(n) time complexity and by using O(1) space.
For example:
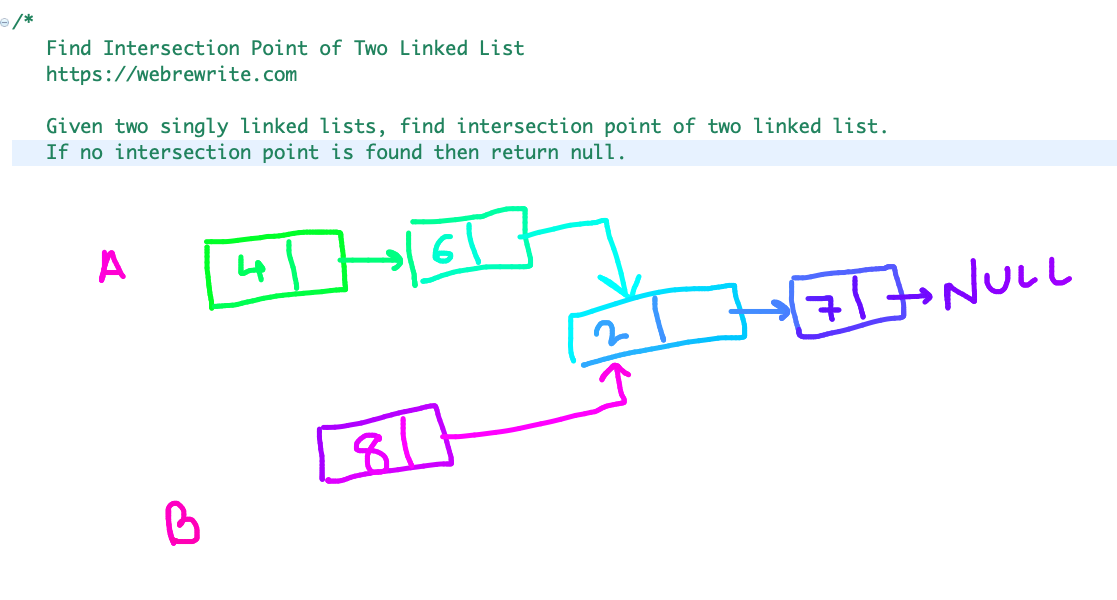
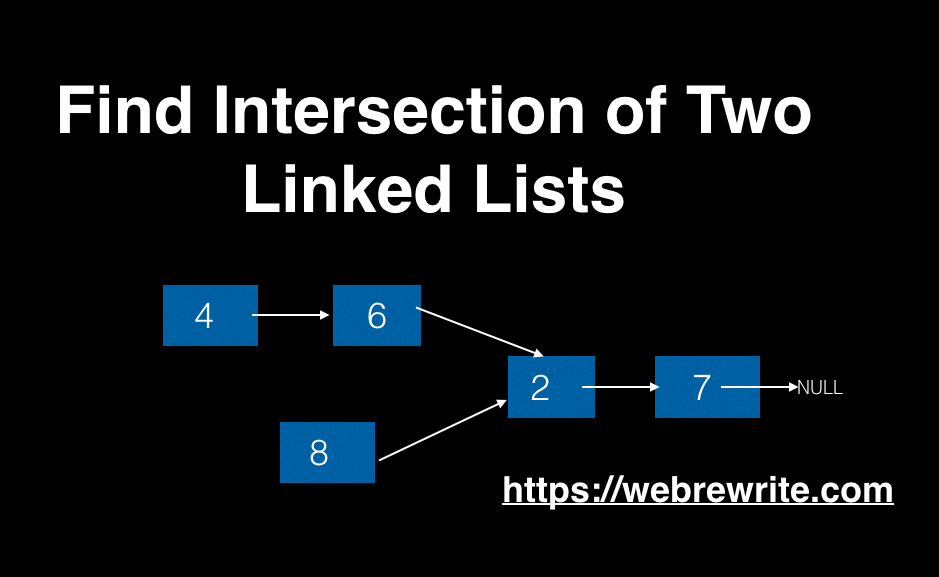
Linked list 1: 4 -> 6 -> 2 -> 7 -> NULL
Linked list 2: 8 -> 2-> 7 -> NULL
In this example, the intersection point of two lists is at node 2.
In this tutorial, I am going to discuss multiple approaches to find the intersection point of two linked lists and their time and spaces complexities to solve this problem.
Programming Questions on Linked List
Programming video tutorials on linked list
If you are not familiar with a the concept of linked list, then check my previous tutorial in which I have explained what is linked list? Difference between array vs linked list and how to insert a node at the beginning of the linked list.
Find the Intersection Point of Two Linked Lists (Brute Force)
The easiest approach is to use two loops to solve this problem. In the first loop, we pick each node from a linked list A and traverse the linked list B to check if any node in linked list B coincides with the node of linked list A.
The time complexity of this approach is O(mn) where m and n is the length of linked list A and B.
The space complexity is O(1).
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
//Find intersection point using brute force approach public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { if(headA == null || headB == null) { return null; } ListNode tempA = headA; //Pick each node of linked list A while (tempA != null) { ListNode tempB = headB; //Find their reference in linked list B while (tempB != null) { //If merge point is found, then return the merge point if (tempA == tempB) { return tempA; } tempB = tempB.next; } tempA = tempA.next; } //If no merge point is found then return null. return null; } |
Find the Intersection of Two Lists using Set – Java Code
The idea here is to traverse a linked list A and store it’s each node reference into a set. Then, check for every node of linked list B whether any node reference present in a set. If reference is found then we have found the intersection or merge point of two linked lists.
The time complexity of this approach is O(m+n) and their space complexity is O(m) or O(n).
We also can use this approach to Detect loop in a linked list.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
//find merge point using set public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { Set<ListNode> st = new HashSet<>(); //Traverse linked list A, put the reference of each node in a set while(headA != null) { st.add(headA); headA = headA.next; } //Traverse linked B for each node check if reference is found while(headB != null) { if(st.contains(headB)) { return headB; } headB = headB.next; } return null; } |
Intersection of Two Linked Lists LeetCode Solution
Let’s improve our solution and solve this problem in O(n) time complexity and without using any extra space.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
//Find intersection of lists without using extra space public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { if(headA==headB) return headA; ListNode first = headA; ListNode second = headB; while(first!=null || second!=null) { first = (first==null) ? headB : first.next; second = (second==null) ? headA : second.next; if(first==second) return first; } return null; } |
In this video tutorial, I have explained the above two methods for finding the intersection of two linked lists.